In today’s digital age, data security is non-negotiable. Whether you’re logging into a website, making an online purchase, or simply browsing, you’re likely benefiting from SSL — a protocol that encrypts data and ensures safe communication over the internet. But how does SSL work exactly?
This comprehensive guide explains everything you need to know about Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), from encryption basics to real-world implementation. Whether you’re a tech professional, website owner, or curious beginner, this post breaks down the technology powering online trust.
What Is SSL?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a standard security protocol for establishing encrypted links between a web server and a browser. It ensures that all data passed between the two remains private and tamper-proof.
While SSL has evolved into TLS (Transport Layer Security), the term “SSL” is still widely used to refer to both protocols.
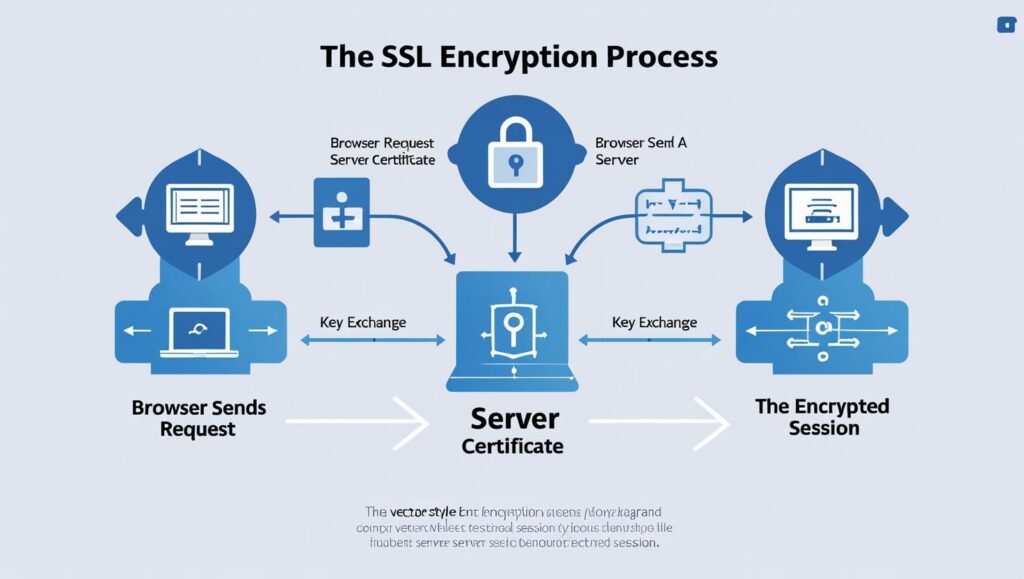
How SSL Works – The Encryption Process
When a user visits an HTTPS-enabled site, SSL uses public key and private key encryption to protect data transmission.
Here’s how SSL works in simple steps:
Browser initiates connection to the server with HTTPS.
Server responds with its SSL certificate (includes public key).
Browser validates the certificate through a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
Session key is generated and encrypted using the server’s public key.
Server decrypts the session key with its private key.
Encrypted communication begins using the shared session key (symmetric encryption).

The SSL Handshake Explained
The SSL handshake is a multi-step protocol that verifies the server’s identity and establishes a secure connection.
Steps of the SSL Handshake:
Client Hello: Browser sends supported SSL versions, cipher suites, and a random number.
Server Hello: Server replies with selected cipher suite, SSL version, and its digital certificate.
Certificate Validation: Browser checks if the certificate is issued by a trusted CA.
Key Exchange: A symmetric session key is created and securely transmitted.
Session Begins: Both sides switch to encrypted communication.
Does SSL Affect SEO?
Yes — SSL significantly impacts SEO:
Ranking Signal: Google prioritizes HTTPS-enabled websites in search results.
Bounce Rate Reduction: Users are less likely to leave a secure site.
Trust in Click-Throughs: HTTPS URLs increase user confidence in SERPs.

Types of SSL Certificates
SSL certificates come in various types depending on the validation level:
| Certificate Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| DV (Domain Validation) | Basic encryption, quick issue time | Blogs, personal websites |
| OV (Organization Validation) | Validates business identity | Business sites |
| EV (Extended Validation) | Highest level, green address bar | E-commerce, financial institutions |
Benefits of SSL for Websites and Users
Implementing SSL offers multiple advantages beyond data encryption:
Data Protection
SSL encrypts sensitive data like login credentials, credit card details, and personal information.
Trust & Credibility
Users are more likely to trust sites with a padlock icon and “HTTPS” in the URL.
Browser Compatibility
Modern browsers alert users when they access a non-secure HTTP site.
Compliance
SSL is mandatory for GDPR, PCI DSS, and other data protection regulations.
SEO Boost
Google confirmed HTTPS is a ranking factor — secure sites may enjoy better visibility.
Common SSL Issues and How to Fix Them
Even with SSL in place, issues may arise. Here are a few common ones:
| Issue | Fix |
|---|---|
| Mixed Content Warning | Ensure all assets (images, scripts) use HTTPS |
| SSL Handshake Failed | Check certificate validity and server configuration |
| Expired SSL Certificate | Renew with your Certificate Authority |
| Self-Signed Certificate Warning | Purchase a trusted CA-signed certificate |
| SSL Port Misconfiguration | Ensure port 443 is open and properly configured |
Conclusion
SSL is the foundation of online trust. From protecting user data to improving search engine rankings, understanding how SSL works is essential for anyone managing or visiting websites. As security threats evolve, implementing SSL (or more accurately TLS) is not just a best practice — it’s a necessity.
Whether you run an e-commerce store, a personal blog, or a SaaS product, installing and maintaining a valid SSL certificate is key to user confidence and data safety.
